Summary
- Change management in health and social care is essential for adapting to ongoing advancements and ensuring quality service delivery.
- Effective communication, stakeholder engagement, and strong leadership are necessary for successful change implementation and overcoming resistance.
- Evaluation and continuous improvement are vital to sustain changes and enhance care delivery, leading to better patient outcomes and staff satisfaction.
- Tools like SWOT analysis and stakeholder mapping support the planning and monitoring of change initiatives, ensuring that the process is structured and efficient.
Change management in health and social care is the structured approach used to plan, implement, and sustain alterations to services, systems, processes, staffing, and ways of working. It involves guiding individuals, teams, and organisations through adjustments that improve care, safety, efficiency, or compliance with new standards. Effective change management ensures that improvements take place smoothly and with minimal disruption for patients, service users, and staff.
In health and social care settings, changes may be small or large. They might involve introducing new technology, adjusting patient care procedures, restructuring teams, or meeting new legal or policy requirements. Without clear organisation and leadership, such changes can cause confusion or reduce quality of service. Change management offers a method to keep changes orderly, well-communicated, and practical.
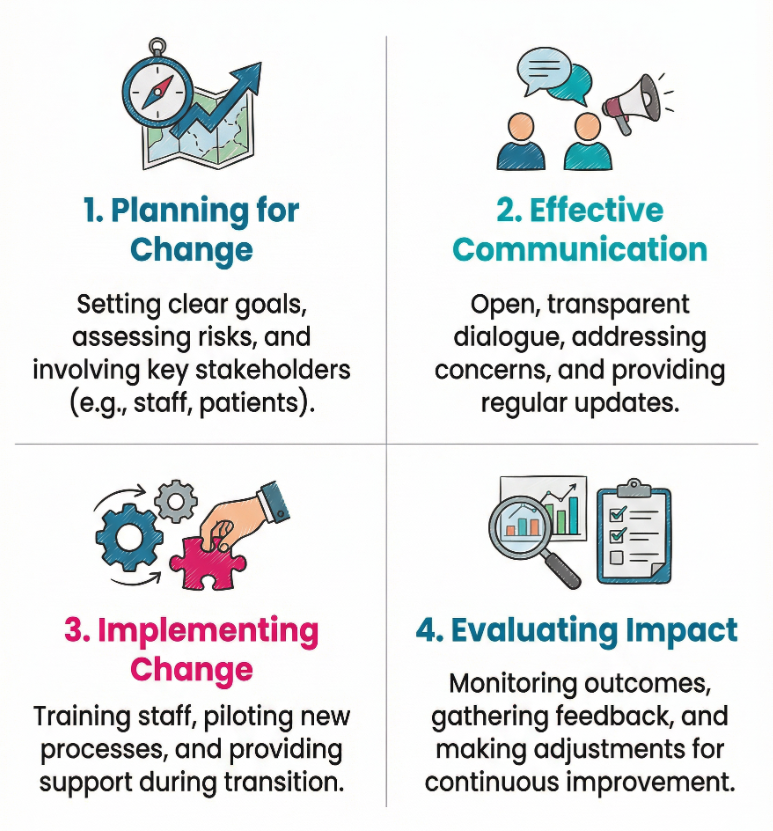
Why Change Happens in Health and Social Care
There are many reasons why change may be required in health and social care settings. These changes often stem from evolving health needs, advances in medical knowledge, or shifts in social care policy. Common drivers include:
- Introduction of new clinical guidelines
- Adoption of improved equipment or technology
- Changes in funding or commissioning arrangements
- Recruitment challenges and staff skill shortages
- Updates to legislation, safeguarding requirements, or health and safety procedures
- Improving patient or service user outcomes
- Addressing inefficiencies or service bottlenecks
By managing change carefully, organisations can respond to these demands without reducing quality of care.
The Principles of Change Management
Change management in health and social care rests on several core principles. These guide how processes, behaviours, and systems are altered and how staff are supported through transitions.
- Clear vision and purpose: Everyone involved should know why the change is happening and what it aims to achieve.
- Strong communication: Information must be shared openly, regularly, and in a way that is easy to understand.
- Staff involvement: Engaging staff early helps them feel part of the process and more willing to support it.
- Training and support: Staff may need new skills or knowledge to adapt to changes successfully.
- Monitoring and feedback: Progress should be reviewed, and adjustments made if part of the change is not working.
- Sustainability: Changes must be maintained over time, not just introduced and then forgotten.
These principles help ensure that changes have lasting impact and do not disrupt service delivery unnecessarily.
Stages of Change Management
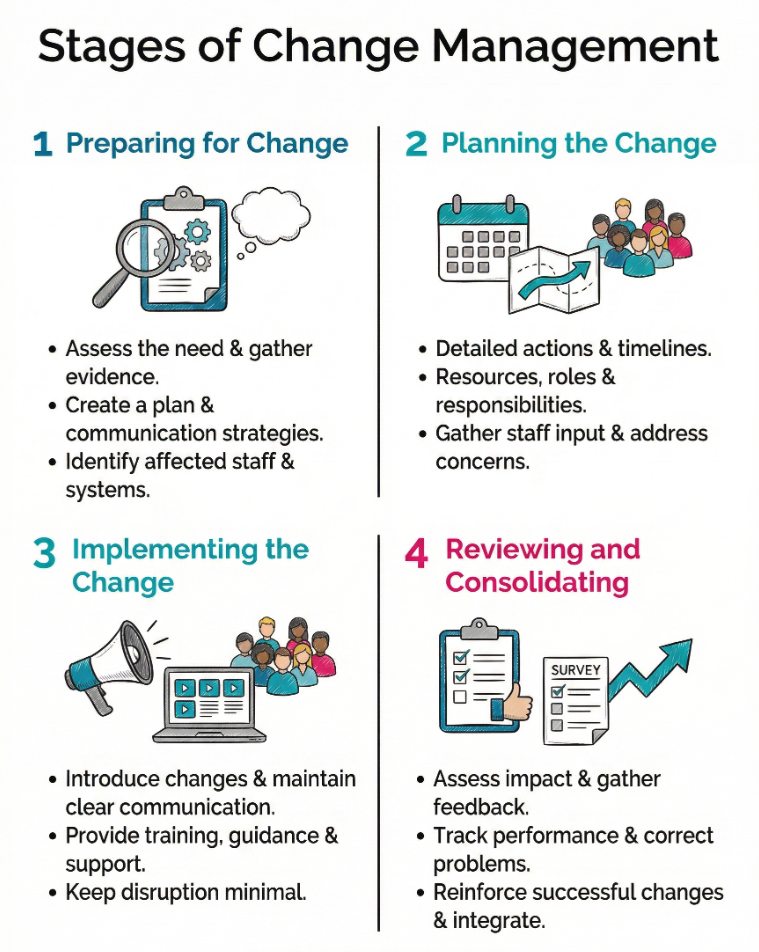
Health and social care organisations often follow clear stages to make change effective. While terminology may vary, the process usually involves:
Preparing for Change
This stage involves assessing the need for change, gathering evidence, and creating a plan. Leaders look at what is driving the change and consider the potential risks and benefits. They prepare communication strategies and identify which staff, departments, or systems will be affected.
Planning the Change
Detailed actions are decided at this stage. Plans include timelines, resources required, roles and responsibilities, and strategies for training. Staff input is gathered, and concerns are addressed before implementation begins.
Implementing the Change
Here, the changes are introduced. Communication becomes constant and clear. Staff receive training or guidance, and managers provide ongoing support. The aim is to keep disruption minimal while making sure everyone understands new processes.
Reviewing and Consolidating
Once changes are in place, their impact is assessed. Feedback is taken from staff and service users, performance measures are tracked, and any problems are corrected. Successful changes are reinforced, and processes are integrated into everyday practice.
The Role of Leadership
Strong leadership is central to change management in health and social care. Leaders set the tone, model positive behaviour, and guide teams through uncertainty. They keep the focus on desired outcomes, handle resistance, and motivate staff to work together.
Good leaders listen to staff concerns, acknowledge challenges, and act on feedback. They provide reassurance when issues arise and recognise achievements during the change process. This maintains morale and builds trust, which can make the difference between success and failure.
Communicating Change Effectively
Communication is often the most important part of managing change. Staff, patients, and other stakeholders need accurate information about what is happening, when, and why. Poor communication can lead to misunderstanding, anxiety, or resistance.
Effective communication involves:
- Using plain language without unnecessary jargon
- Providing updates regularly
- Allowing opportunities for questions and discussion
- Using different formats such as meetings, emails, posters, or online systems
- Explaining how roles and responsibilities will be affected
When people know what to expect, they are more likely to cooperate and adapt.
Handling Resistance to Change
Resistance to change is common in any workplace, especially in health and social care where routines and standards are important for safety and reliability. Resistance may be emotional, such as fear of losing a familiar role, or practical, such as concern about increased workload.
The best approach to managing resistance is to understand its causes and address them directly. This may involve listening to concerns, showing evidence of benefits, offering extra training, or gradually phasing in changes. Respecting staff views and involving them in solutions can greatly reduce opposition.
Staff Involvement and Engagement
Staff who are actively involved in planning and implementing change tend to support it more strongly. Engagement can include consultation meetings, surveys, working groups, or pilot projects. Participation allows staff to shape changes in ways that make sense for their workplace and service users.
By involving staff, organisations can identify practical issues that may otherwise be overlooked. It also shows respect for professional expertise and encourages a culture of teamwork.
The Human Side of Change Management
Health and social care work often involves stress and emotional demands. Change can add to these pressures. The human side of change management considers the feelings, values, and personal circumstances of staff and service users.
Managers need to recognise that change affects people differently. Some may feel anxious or confused, while others might be excited by new opportunities. Supporting staff through clear communication, empathy, and understanding can ease transitions.
Offering wellbeing support, peer mentoring, or flexible implementation schedules may help staff cope with change more easily.
Measuring the Success of Change
Once a change has been put into practice, it must be assessed. Measurement can focus on outcomes for patients, service users, or staff. It might include reductions in waiting times, improvements in care quality, or better staff retention.
Feedback from service users and staff can highlight strengths and areas for improvement. Comparing performance before and after the change provides evidence of whether aims were met.
Assessment should be ongoing, as some changes take time to produce measurable results.
Examples of Change in Health and Social Care
Changes in health and social care can vary widely. Examples include:
- Moving from paper-based records to electronic patient records
- Introducing new safeguarding procedures in care homes
- Creating new specialist roles to meet changing patient needs
- Restructuring services to meet budget constraints
- Implementing infection prevention measures after an outbreak
Each type of change requires careful planning, communication, and monitoring to avoid disruption and maintain service quality.
What are the Challenges in Change Management?
Common challenges include:
- Resistance from staff or service users
- Lack of resources such as staff time, funding, or equipment
- Overlapping priorities that make it hard to focus on one change
- Confusion caused by poor communication
- Difficulty sustaining improvements long term
Addressing these challenges requires strong leadership, flexibility, and continued communication after initial changes have been made.
Building a Culture That Supports Change
Organisations that view change as a normal part of improvement often manage it more smoothly. This type of culture values innovation, learning, and openness. Staff are more willing to try new approaches when they trust that their voices will be heard.
Building this culture involves rewarding creativity, sharing success stories, and encouraging problem-solving. Training staff in change processes can also help them feel more confident about future adjustments.
Final Thoughts
Change management in health and social care is a planned, structured way of achieving improvements without causing unnecessary disruption. It requires leadership, clear communication, staff involvement, and an understanding of how change affects both service users and workers. By planning carefully, introducing changes gradually, and reviewing their impact, organisations can make progress that benefits everyone involved.
Successful change management is not just about systems and processes. It is about people. Supporting staff and service users through periods of transition increases the likelihood that new ways of working will be accepted and maintained. With a strong commitment to planning, communication, and evaluation, health and social care services can continue to meet the needs of those who rely on them.
Further Learning and References
- The Change Model Guide – NHS England
Introduces a practical eight-component framework co-produced with health and care staff to guide structured, scalable change across any level—from small projects to system-wide transformation. - Change Management – Health Education England Learning Zone
Defines change management as a structured approach to implementing new ways of working in order to minimise disruption, manage uncertainty, and support sustainable improvement. - Managing the Human Dimensions of Change – NHS Improvement
Highlights the frequently overlooked ‘soft’ or people-centred aspects of change and stresses the importance of understanding emotional responses and engaging stakeholders to avoid resistance. - Where Do Models for Change Management, Improvement and Implementation Fit Within Healthcare? – PMC (NCBI)
Offers a systematic review positioning change-management models as structured, end-to-end processes—from inception to benefits realisation—and exploring how they can complement improvement and implementation science methodologies. - Creating Conditions for Change & Integration – HSE (Ireland)
Emphasises the essential role of people, culture, and readiness in health and social care transformation, promoting collective leadership, shared values, evidence use, and stakeholder engagement as foundational to successful change.
Glossary and Key Terms
- Change Management: This refers to the process of planning and implementing changes within an organisation. It helps ensure that transitions happen smoothly and effectively.
- Stakeholder: A stakeholder is anyone who has an interest in the change. This includes staff, patients, families, and partner organisations.
- Resistance to Change: This term describes the reluctance of individuals or groups to accept new methods or practices. It can stem from fear or attachment to existing processes.
- SWOT Analysis: This is a tool used to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a proposed change. It helps organisations understand their current situation.
- Cultural Barriers: These are obstacles that arise from the existing beliefs and behaviours within an organisation. They can hinder the acceptance of new changes.
- Communication: This is the act of sharing information clearly. Good communication helps everyone understand the reasons for change and its benefits.
- Leadership: Effective leadership involves guiding teams through change. Leaders set goals, motivate others, and manage any resistance that arises.
- Training and Development: This refers to ongoing education for staff. It ensures that they are equipped with the skills needed to adapt to new processes or systems.
- Evaluation: Evaluation involves assessing the impact of changes after implementation. It helps determine if goals have been met and if further adjustments are needed.
- Change Champion: A change champion is a person who advocates for change within an organisation. They support the process and help motivate others to embrace new practices.
Subscribe to Newsletter
Get the latest news and updates from Care Learning and be first to know about our free courses when they launch.






